AV Glossary
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z3D Compatible
3D compatible means that one or more of the 3D compliant formats are supported by the display or repeater device.
3D Compliant
Mandatory formats the display (sink) or repeater device must support to be HDMI 1.4a compliant are:For movie content – Frame Packing 1080p@ 23.98/24HzFor gaming content – Frame Packing 720p@50/60Hz Frame Packing 720p@ 59.94/60HzFor broadcast content – Side-by-Side Horizontal 1080i@50/60Hz Side-by-Side Horizontal 1080i@ 59.94/60Hz Top-and-Bottom 720p@50/60Hz Top-and-Bottom [email protected]/60Hz Top-and Bottom [email protected]/24Hz
4K Resolution
Initially this referred to approximately 4,000 pixels of horizontal resolution for digital cinemas where 4K =4096 x 2160 or 8.8 megapixels. 4K related to HDMI refers to 3840 x 2160 or 8.3 megapixels which is 4 times the 1920 x 1080 or 2.1 megapixel HDTV standards. 4K has 4 times the number of pixels as 1080p.
ARC
Audio Return Channel - If an HDTV has a built-in tuner, DVD player, or other digital content source, the Audio Return Channel allows the TV to send audio data "upstream" to your A/V receiver, eliminating the need for a separate audio cable in this type of configuration. Audio Return Channel-enabled TVs can either send or receive audio via the HDMI link, giving you greater flexibility in how you set up your home theater equipment and making a separate upstream audio link unnecessary.
AVI Infoframes
From a high level, the AVI Infoframes flow from the source to the display every two video fields as a part of the video content in the TMDS lines. The display uses the Infoframes information to specifically identify the format of the audio and video streams sent to it at that moment and how it is supposed to render it at that moment. They dynamically define audio and video format information based on the actual material being played back.
AVR
Audio Video Receivers are one of the many consumer electronics components typically found within a home theatre system. Their primary purpose is to amplify sound from a multitude of possible audio sources as well as route video signals to the user's TV from various sources. The user may program and configure a unit to take inputs from devices such as DVD players, VCRs etc. and easily select for which source he or she wants to route to their TV and have sound output.
Analog Video Formats
Composite-Video, Component-Video (YPbPr), S-Video and VGA
Aspect Ratio
The aspect ratio of an image describes the proportional relationship between its width and its height. It is commonly expressed as two numbers separated by a colon, as in 16:9.
Audio Return Channel
If an HDTV has a built-in tuner, DVD player, or other digital content source, the Audio Return Channel allows the TV to send audio data "upstream" to your A/V receiver, eliminating the need for a separate audio cable in this type of configuration. Audio Return Channel-enabled TVs can either send or receive audio via the HDMI link, giving you greater flexibility in how you set up your home theater equipment and making a separate upstream audio link unnecessary.
Audio Video Receivers
Audio Video Receivers are one of the many consumer electronics components typically found within a home theatre system. Their primary purpose is to amplify sound from a multitude of possible audio sources as well as route video signals to the user's TV from various sources. The user may program and configure a unit to take inputs from devices such as DVD players, VCRs etc. and easily select for which source he or she wants to route to their TV and have sound output.
CEC
Consumer Electronics Control (CEC) is an HDMI feature designed to allow the user to command and control up-to 15 CEC-enabled devices, that are connected through HDMI, by using only one of their remote controls (for example by controlling a television set, set-top box, and DVD player using only the remote control of the TV). CEC also allows for individual CEC-enabled devices to command and control each other without user intervention.
Color Depth
Color depth is the number of bits used to indicate the color of a single pixel in a bitmapped image or video frame buffer. This concept is usually quantified as bits per pixel (bpp), which specifies the number of bits used. Color depth expresses how finely levels of color can be expressed.
Color Space
A color model is an abstract mathematical model describing the way colors can be represented. Common color spaces based on the RGB model include sRGB, Adobe RGB and ProPhoto RGB. xvYCC is a new international digital video color space standard published by the IEC which extends the gamut beyond the RGB models. YCbCr is the digital form of YPbPr used widely in video and image compression schemes such as MPEG and JPEG.
Consumer Electronics Control
Consumer Electronics Control (CEC) is an HDMI feature designed to allow the user to command and control up-to 15 CEC-enabled devices, that are connected through HDMI, by using only one of their remote controls (for example by controlling a television set, set-top box, and DVD player using only the remote control of the TV). CEC also allows for individual CEC-enabled devices to command and control each other without user intervention.
DCP, LLC
Digital Content Protection LLC (DCP) is an organization that licenses technologies for protecting premium commercial entertainment content. High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection (HDCP) is a specification developed by Intel Corporation to protect digital entertainment content across digital interfaces. The HDCP specification provides a robust, cost-effective and transparent method for transmitting and receiving digital entertainment content to compliant digital displays.
DDC
The Display Data Channel (DDC) is a communication channel between a source and display based on a special serial data bus called the I²C bus. DDC is used by the HDMI source device to read the EDID data from the HDMI display device to learn what audio/video formats it supports. The DDC channel is actively used for High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection (HDCP).
DRM
Digital Rights Management (DRM) technologies attempt to give control to the seller of digital content or devices after it has been given to a consumer. For digital content this means preventing the consumer access, denying the user the ability to copy the content or converting it to other formats. For devices this means restricting the consumers on what hardware can be used with the device or what software can be run on it.
DVI
Digital Visual Interface (DVI) was developed to create an industry standard for the transfer of digital video content. The interface is designed to transmit uncompressed digital video and can be configured to support multiple modes such as DVI-D (digital only), DVI-A (analog only), or DVI-I (digital and analog). Featuring support for analog connections as well, the DVI specification provides optional compatibility with the VGA interface through a passive adapter.
Deep Color
In color reproduction, the gamut is a certain complete subset of colors. The most common usage refers to the subset of colors which can be accurately represented in a given circumstance, such as within a given color space or by a certain output device. Deep color is a ""gamut"" comprising a billion or more colors. The xvYCC, sRGB, and YCbCr color spaces can be used with deep color systems. Deep color supports 30/36/48bit for three RGB colors.
Digital Video
Digital video is a type of digital recording system that works by using a digital rather than an analog video signal. Digital video comprises a series of bitmap digital images displayed in rapid succession at a constant rate. In the context of video, these images are called frames. We measure the rate at which frames are displayed in frames per second (FPS). Each bitmap digital image comprises a raster of pixels. If the frame has a width of W pixels and a height of H pixels we say that the frame size is W x H. Pixels have only one property, their color. The color of a pixel is represented by a fixed number of bits. The more bits the more subtle variations of colors can be reproduced. This is called the color depth of the video.
DisplayPort
DisplayPort is a digital display interface developed by the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA). The interface is primarily used to connect a video source to a display device such as a computer monitor, though it can also be used to transmit audio, USB, and other forms of data
EDID
Extended display identification data (EDID) is a data structure provided by a digital display to describe its capabilities to a video source (e.g. graphics card or set-top box). It is what enables a source device to know what kind of display it is connected to. EDID is defined by a standard published by the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA). The EDID includes manufacturer name and serial number, product type, phosphor or filter type, timings supported by the display, display size, luminance data and (for digital displays only) pixel mapping data.
Ethernet
Ethernet is a family of computer networking technologies for local area networks (LANs). The Ethernet standards comprise several wiring and signaling variants of the OSI physical layer in use with Ethernet. The original 10BASE5 Ethernet used coaxial cable as a shared medium. Later the coaxial cables were replaced by twisted pair and fiber optic links in conjunction with hubs or switches. Data rates were periodically increased from the original 10 megabits per second to 100 gigabits per second.
Frame Rate
Frame rate is the frequency (rate) at which an imaging device produces unique consecutive images called frames. The term applies equally well to film and video cameras, computer graphics, and motion capture systems. Frame rate is most often expressed in frames per second (FPS) and is also expressed in progressive scan monitors as hertz(Hz). There are three main frame rate standards in the TV and digital cinema business: 24p, 25p, and 30p. However, there are many variations on these as well as newer emerging standards.
HD-SDI
Serial Digital Interface (SDI) and High-Definition Serial Digital Interface (HD-SDI) are a family of video interfaces standardized by SMPTE (The Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers). HD-SDI provides a higher data rate than SDI which is used for High Definition video signals. SDI and HD-SDI are currently only available in professional video equipment; various licensing agreements, restricting the use of unencrypted digital interfaces to professional equipment, prohibit their use in consumer equipment.
HDBaseT
HDBaseT, supported by The HDBaseT Alliance, is a consumer electronic (CE) connectivity technology for long-distance transmission of uncompressed high-definition video (HDMI), HD multi-channel audio, 100BaseT Ethernet, high-power (PoH – Power over HDBaseT) and RS232/IR control signals, via a 100m Cat5e/Cat6 cable with RJ45 modular connectors commonly used in Ethernet LAN
HDBaseT-Lite
A limited version of HDBaseT which supports high-definition video (HDMI), HD multi-channel audio, and RS232/IR control signals, via a 70m Cat5e/Cat6 cable.
HDCP
High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection (HDCP) is a form of digital copy protection developed by Intel Corporation to prevent copying of digital audio and video content as it travels across connections. Types of connections include DisplayPort (DP), Digital Visual Interface (DVI), and High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI). The system is meant to stop HDCP-encrypted content from being played on unauthorized devices or devices which have been modified to copy HDCP content.
HDCP Encryption
Before sending data, an HDCP transmitting device checks that the receiver is authorized to receive it. If so, the transmitter encrypts the data to prevent eavesdropping as it flows to the receiver.
HEAC
HDMI Ethernet Audio Control (HEAC) is a combined acronym for HEC and ARC.
HEC
HDMI Ethernet Channel (HEC) provides a bidirectional Ethernet communication at 100 Mbit/s over an HDMI cable.
HPD
The Hot Plug Detect (HPD) channel senses plugging in or unplugging of an HDMI device, re-initializing the HDMI link if necessary.
PoH
Power over HDBaseT (PoH) supplies up to 100W of power down the twisted pair cable which can be utilized to power a remote TV or HDBaseT receiver device.
Refresh Rate
The refresh rate (most commonly the "vertical refresh rate") is the number of times in a second that display hardware draws the data. This is distinct from the measure of frame rate in that the refresh rate includes the repeated drawing of identical frames, while frame rate measures how often a video source can feed an entire frame of new data to a display. For example, most movie projectors advance from one frame to the next one 24 times each second. But each frame is illuminated two or three times before the next frame is projected using a shutter in front of its lamp. As a result, the movie projector runs at 24 frames per second, but has a 48 or 72 Hz refresh rate.
S/PDIF
Sony/Philips Digital Interconnect Format (S/PDIF) is a type of digital audio interconnect cable used in consumer audio equipment to output audio over reasonably short distances. The signal is transmitted over either a coaxial cable with RCA connectors or a fiber optic cable with TOSLINK connectors.
SDI
Serial Digital Interface (SDI) and High-Definition Serial Digital Interface (HD-SDI) are a family of video interfaces standardized by SMPTE (The Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers). HD-SDI provides a higher data rate than SDI which is used for High Definition video signals. SDI and HD-SDI are currently only available in professional video equipment; various licensing agreements, restricting the use of unencrypted digital interfaces to professional equipment, prohibit their use in consumer equipment.
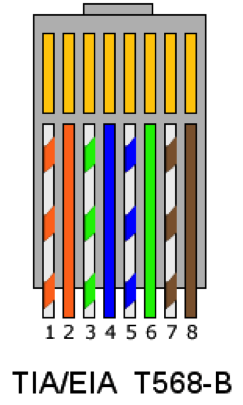
T568B
T568B defines the pin out, or order of connections, for wires in an RJ45 eight-pin modular connector plugs and sockets.

TMDS
Transition-Minimized Differential Signaling is a technology for transmitting high-speed red, green, blue and timing digital serial data and is used by the DVI and HDMI video interfaces.
VESA
Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA) is an international standards body for computer graphics. VESA's initial goal was to produce a standard for 800×600 SVGA resolution video displays. Since then VESA has issued a number of standards, mostly relating to the function of video peripherals in personal computers.
VGA
Video Graphics Array (VGA) refers specifically to the display hardware first introduced with the IBM PS/2 line of computers in 1987, but through its widespread adoption has also come to mean either an analog computer display standard, the 15-pin D-subminiature VGA connector or the 640×480 resolution itself.
WHDI
Wireless Home Digital Interface (WHDI) is a consumer electronic standard for a wireless HDTV connectivity throughout the home. WHDI enables delivery of uncompressed high-definition video over a wireless radio channel connecting any video source (computers, mobile phones, Blu-ray players etc.) to any compatible display devices.
 CXUnify
CXUnify